 Thayer's Gull (thayeri)
Thayer's Gull (thayeri)
(last update: January 22, 2013)
Thayer's Gull 1cy December (1st cycle)
FIRST PREBASIC MOLT IN HERRING, THAYER'S, AND GLAUCOUS-WINGED GULLS
STEVE N. G. HOWELL AND JON R. KING
Point Reyes Bird Observatory
4990 Shoreline Highway
Stinson Beach, California 94970 USA
CHRIS CORBEN
P.O. Box 2323
Robherr Park, California 94927 USA
IN: J. Field Ornithol., 70(4):543-554, 1999
Abstract.
We made regular field observations over three winters of first-year Herring Gulls (Larus argentatus smithsonianus) , Thayer's Gulls (L. thayeri), and Glaucous-winged Gulls (L. glaucescens) in order to document the timing of first prebasic molts. The first prebasic molt of North American Herring Gulls starts between September and February. Most resident birds on the Atlantic coast undergo extensive first prebasic molt by late November, while some migrants wintering in California do not start molt until January or later. The onset of first prebasic molt in 90% of Thayer's Gulls is not until January or later, and some birds migrating north in March appear to be still in juvenal plumage. Initiation of first prebasic molt in Glaucous-winged Gulls spans late October to March, such that some birds have largely finished molting before others start. Our findings differ from or clarify those of previous authors. We sugges that differences in molt timings within and among taxa of large gulls reflect the nature of their migrations. Largely resident or short-distance migrant populations can start molt up to several months earlier than those populations that undertake longer migrations. Most molt studies rely heavily upon specimens. However, while museum collections may have adequate series of passerines, this is rarely true of larger birds such as gulls. Critical field observations of species that lend themselves to field study, in combination with documentary photographs and judicious collection of voucher specimens, can more easily provide adequate samples to follow molt in a population.
|
|
Molt, along with reproduction and migration (in migratory species), is one of two or three fundamental energy-demanding processes in the life cycle of birds. Thompson and Leu (1994) summarized how an understanding of molt is important for addressing many basic and applied issues of avian biology. In comparison to reproduction and migration, however, molt has received disproportionately little attention in the scientific literature (review by Thompson and Leu 1994), and most recent molt studies have focused on passerines and "near passerines" (e.g., Pyle 1997, and references therein). Indeed, molt in most species of gulls has received little attention since the seminal work of Dwight (1925). Therefore, we review the timing of the first prebasic molts of three migratory large gulls, Herring Gull (Larus argentatus), Thayer's Gull (L. thayeri), and Glaucous-winged Gull (L. glaucescens) that winter regularly in California. All three species occur commonly in central California from October-March, with Glaucous-winged Gulls arriving earliest and Thayer's Gulls latest (Shuford et al. 1989; pers. obs.).
The Herring Gull is widespread in the northern hemisphere. Marked geographic variation in the Old World has led some authors to split the Herring Gull complex into as many as six species (e.g., see discussions by Beaman 1994, Kennerly et al. 1995). However, except in westernmost Alaska (where the Siberian form vegae occurs), the Herring Gull is represented in the Americas by the single, widespread subspecie smithsonianus. Some authors (Devillers 1983a, Kennerly et al. 1995) consider vegae (Vega Gull) a species separate from other Herring Gulls, but smithsonianus has been conspicuously absent to date from taxonomic studies involving the Herring Gull complex.
To our knowledge, no molt studies have focused specifically upon North American Herring Gulls (cf. Dwight 1925, Pierotti and Good 1994). Dwight (1925) based his descriptions of plumage and molt in this species on samples from North America, Siberia, and England, obscuring the molt schedule of any one taxon. Compounding the problem, Dwight's "first-winter" Herring Gull reference specimen from England has been re-identified subsequently as a Lesser Black-backed Gull L. fuscus graellsii (Poor 1946). Dwight (1925) described the first prebasic molt as a slow and rather incomplete replacement starting on average in September, October, or November (rarely as late as mid-winter) and ending by December or sometimes later. In some birds he concluded that the first prebasic and first prealternate molts overlapped, the latter occurring in March, April, and May.
Thayer's Gull breeds in Arctic Canada and has experienced a checkered taxonomic history, which remains unresolved. It was described originally as a full species (Brooks 1915) but shortly thereafter considered a subspecies of the Herring Gull (AOU 1957, Dwight 1925), based upon the superficial similarity of adult plumages. More recent studies (Macpherson 1961, Godfrey 1986, Snell 1989) have supported a closer relationship to the Iceland Gull (L. glaucoides), with which Thayer's is often considered conspecific (Devillers 1983b, Godfrey 1986). The AOU (1998) recognized Thayer's Gull as a full species, based upon the discredited work of Smith (1966; see Snell 1989, 1991). We are aware of no study that has specifically addressed molt in Thayer's Gull. Lehman (1980) proposed that Thayer's Gulls molt into first basic plumage by October or, rarely, as late as November. McGeehan and Garner (1997) deduced from photographs that "Thayer's Gulls appear to have a distinct juvenile plumage which is still unmoulted on the winter quarters well into November," but they were unable to pursue the subject in more detail.
The Glaucous-winged Gull is a monotypic gull of the North Pacific. Despite extensive interbreeding with Western Gulls (L. occidentalis) in the Pacific Northwest (Bell 1996, 1997; Hoffman et al. 1978), regular interbreeding with Herring and Glaucous (L. hyperboreus) gulls in Alaska (Swarth 1934, Williamson and Peyton 1963), and at least some interbreeding with the Slaty-backed Gull (L. schistisagus) in Siberia (Grabovsky et al., unpubl. data), it is generally considered a full species (Godfrey 1986, AOU 1998). Dwight (1925) described the first basic plumage as attained by a partial molt during August-October, Verbeek (1993) questioned some of Dwight's conclusions but provided no new data on immatures and stated "molts and plumages not well studied."
Incidental prior observations by Corben brought into question much conventional wisdom concerning the timing of first prebasic molt in large gulls, in particular for how long full juvenal plumage may be retained. Our study aimed to quantify and describe this molt in three species for which we could obtain adequate samples, and to compare our findings with previous published work.
STUDY AREA AND METHODS
From October 1997-March 1998 we conducted regular field observations at Bolinas, Marin Co. (37ø55'N, 122ø41'W), and Petaluma, Sonoma Co. (38ø29'N, 122ø37'W), central California. Both sites are bathing and loafing areas where gulls gather and can be viewed for prolonged periods at close range. We visited one or both of these sites at least once every 10 d in early (1-10), mid (11-20), and late (21-end) month, and we attempted to make close-range observations (often to within 10-20 m, viewed through 30x-60x telescopes) of at least ten first-year individuals of all three species per visit. We took documentary photographs throughout the winter and salvaged voucher specimens (one Herring, three Thayer's, one Glaucous-winged) for examination; these specimens were deposited (accession number 5330) at the California Academy of Sciences.
Our data from Bolinas and Petlauma were supplemented by less regular observations at the following sites in central California: Fort Bragg, Mendocino Co.; Cordell Bank and Bodega Bay, Sonoma Co.; Tomales Bay and Abbott's Lagoon, Marin Co.; Lake Merritt, Alameda Co.; South East Farallon Island, San Francisco Co.; Hidden Lake and Lake Cunningham, Santa Clara Co.; and Monterey, Monterey Co. In addition, we gathered molt data on a less regular basis between November 1996-April 1997 at Bolinas Lagoon, Lake Merritt, and Petaluma, and Howell and Corben collected data for October 1998-March 1999 at Bolinas Lagoon, Petaluma, and Bodega. For Herring Gulls, Howell also made observations of birds on the Atlantic coast in Massachusetts and New Jersey (September-October 1997) and in Baja California, Mexico (February 1998). We further solicited data and photographs from east coast observers (see Acknowledgments) for November 1997-February 1998, and we examined specimens at museums (American Museum of Natural History; Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University; Museum of Vertebrate Zoology, University of California, Berkeley; California Academy of Sciences) to confirm characters of juvenal plumage based upon birds collected at and near breeding grounds.
We checked all birds for any sign of first prebasic molt in all visible tracts of head, body, and wings. The contrast between first-basic feathers (usually darker and grayer) and juvenal feathers (usually browner or faded to whitish) was most easily detected in the mantle and scapular tracts, although close range observations enabled us to detect molt on the head, neck, and underparts in many individuals. We estimated the percentage area of first-basic feathers in five areas: the head/neck, chest/underparts, mantle (defined here as the interscapular area), scapulars, and upper-wing coverts. Feather contrasts in the head, neck, and underparts could be difficult to see at other than close range, however, and we were unable to obtain complete molt data for all birds. Through March 1999, we recorded molt data in all visible tracts for 182 of 262 Herring Gulls, 221 of 289 Thayer's Gulls, and 228 of 365 Glaucous-winged Gulls, and data on scapular molt for all of these birds. Because the scapulars were easy to observe and their replacement appeared to reflect the overall span of first prebasic molt in other tracts (see Results), we used them as an index to the progression of molt (Figs. 1-3). We recognize that in some cases (less than 5% of birds, however) a few feathers from the head, chest, or mantle might be replaced before the first scapulars. In addition, it is possible that all of the scapulars might be replaced while juvenal feathers remained on other parts of the body, although we saw no birds that had replaced all of their scapulars prior to northward migration.
Without large populations of individually marked birds it is impossible to know for how many of the same birds we recorded data on different dates. Many individuals could be recognized by virtue of plumage or bill markings, however, and we attempted to avoid making repeat observations of the same individuals within a 10-d period. Based upon recognition of individual birds, the two sites we sampled regularly showed a marked and perhaps almost continual turnover of all three species throughout the winter, and our results should be viewed accordingly.
The species-level identification of large gulls is among the most problematic concerns of North American field ornithology. The optimal conditions for observation at our study sites meant that specific identification of non-hybrid gulls (see below) was rarely problematic. Herring Gulls and Thayer's Gulls were distinguished by a suite of structural and plumage characters (Gosselin and David 1975, Lehman 1980, and Grant 1986). During all days in the field we encountered gulls of presumed hybrid origin. Presumed hybrid Glaucous-winged x Western Gulls and Glaucous-winged x Herring Gulls combined comprised up to 20% of first-year birds present at our study sites (Howell, unpubl. data), and we excluded from our data any birds we judged subjectively to be hybrids.
RESULTS
Sequence of molt and appearance.
With few exceptions, the first signs of first prebasic molt in all three species were the replacement of one or two shorter scapulars. In very few birds (one Herring, five Thayer's), however, the first feathers replaced were a few mantle feathers, while others (two Thayer's, three Glaucous-winged) showed a few first-basic feathers at the sides of their chest and/or on the head before any mantle feathers or scapulars had been molted. From mid-winter into their first spring, approximately 60-70% of Herring and Glaucous-winged and 10-25% of Thayer's Gulls showed whitening of the head, and less often the whole head, neck, and upper chest. Close scrutiny of such birds revealed that this whitening represented wear and bleaching of unmolted juvenal feathers rather than the attainment of new, whiter feathers, as has usually been assumed or implied (e.g., Grant 1986). On some birds the whiter nape contrasted sharply with the darker, less-exposed feathers of the lower hindneck; on other birds, the whiter head, foreneck, and upper chest contrasted quite abruptly with the dusky belly whose narrow pale tips had abraded to expose extensive dark bases. Thus, birds in late winter could appear both darker bellied and whiter headed than in early winter, although both changes in appearance were due to plumage wear rather than to molt.
Timing and extent of molt.
Timing and, to a lesser degree, extent of the first prebasic molt varied markedly within and between species (see below). However, we detected no replacement of wing coverts, tail coverts, flight feathers, rump, or belly feathers during the first prebasic molt, which was limited to head and body tracts.
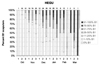 Figure 1 Timing of first prebasic molt in Herring Gulls (HEGU) wintering in central
California. Figure 1 Timing of first prebasic molt in Herring Gulls (HEGU) wintering in central
California. |
Herring Gull.
Molt started with the shorter scapulars and mantle, and usually 20-30% of the anterior scapular area was replaced before first-basic mantle feathers appeared. The first signs of molt away from the mantle and scapulars were on the sides of the chest adjacent to the bend of the wing and, less obviously, on the lores, crown, auriculars, sides of the neck, and lower hindneck adjacent to the mantle. Molt progressed at highly variable rates through the mantle, scapulars, chest, flanks, head, and sides of the neck, with feathers of the nape and upper hindneck molted last or retained through later winter. About 10-20% of birds replaced up to 50% of the mantle and scapular area before we detected molt in other tracts. Furthermore, in about 10-20% of birds, replacement of scapulars and mantle through March achieved 60-90%, but few feathers (1-5%) were replaced in the head, neck, chest, and flanks. On all birds, the belly appeared to be covered by mostly, if not entirely, juvenal feathering through late winter. Molt of the scapulars was protracted over several months such that we saw no birds in which all scapulars had been replaced by the end of March. In particular, some of the longest scapulars were still juvenal feathers by the time birds departed in spring.
Herrings Gulls showed considerable variation in the extent and timing of their first prebasic molt. Through early December, over 50% of first-year Herring Gulls retained apparently full juvenal plumage, with the ratio of these birds dropping to around 30% by early January (Fig. 1). The latest bird with apparently full juvenal plumage was seen in mid-February. An interesting dichotomy became apparent over the winter in the relative extent of first-prebasic molt in Herring Gulls: in January and February, about half the birds had 0-10% (mean 3.2%) first-basic scapulars, while half had 30-93% (mean 59.4%) first-basic scapulars (Fig. 1). A similar difference was also noted for birds in Baja California (e.g., of ten birds during 20-22 Feb. 1998, three had 0-5% first-basic scapulars, while seven had 65-95% first-basic scapulars).
In New England, 70% of 50 presumed locally bred, first-year Herring Gulls observed in Massachusetts and New Jersey during late September to mid-October showed obvious signs of molt into first-basic plumage (Howell, pers. obs.), and by late November, most if not all resident New Jersey birds had replaced most of their juvenal mantle and scapular feathers (D. A. Sibley, pers. comm.). Subsequent winter observations in New Jersey and Connecticut revealed a few birds (less than 10% of 300 seen) from November through late January that had attained only 0-10% first-basic mantle and scapulars (D. A. Sibley, pers. comm.).
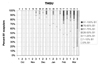 Figure 2 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Thayer's Gulls (THGU)
wintering in central California. Figure 2 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Thayer's Gulls (THGU)
wintering in central California. |
Thayer’s Gull.
This species showed an overall similar molt sequence to that described for the Herring Gull, but averaging considerably later and more restricted. Thus, through March, while replacement of scapulars and mantle had achieved 60-90% in the most advanced birds, few feathers (1-5%) had been replaced in the head, neck, chest, and flanks of all Thayer's Gulls.
The first birds noted with first prebasic molt were in late November, but through December over 90% of Thayer's Gulls were still in juvenal plumage. January marked a fairly rapid onset of the first prebasic molt in around 30% of Thayer's Gulls (Fig. 2), although over 50% of birds through early March still appeared to be in full juvenal plumage, and we saw one such bird in early April. Interestingly, many of these late winter juveniles did not have heavily abraded plumage.
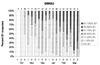 Figure 3 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Glaucous-winged Gulls
(GWGU) wintering in central California. Figure 3 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Glaucous-winged Gulls
(GWGU) wintering in central California. |
Glaucous-winged Gull.
Rarely (0.5% of birds) was more than 10% of the scapular area molted before some first-basic mantle feathers appeared, and usually (92% of birds) not until at least 10% of the mantle and scapular area had molted did we detect first-basic feathers on the head and body. The first signs of molt away from the mantle and scapulars usually were in the face and/or on the sides of the chest, much as in Herring Gull, as was the subsequent progression of molt.
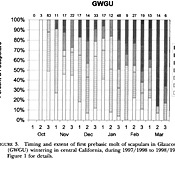
The initiation of the first prebasic molt in Glaucous-winged Gulls spanned a wide period from October-March, and the last bird in full juvenal plumage was seen in mid March (Fig. 3). Through mid-December there appeared to be a steady decrease in the numbers of birds in full juvenal plumage, countered by a steady increase in the percentage attainment of first-basic scapulars (Fig. 3). In late December 1997 and early January 1998, however, there was an influx of Glaucous-winged Gulls into central California, and our sample then included 26.5% in full juvenal plumage and 40.5% with only a few first-basic scapulars. This influx saw an arrival of apparent Glaucous-winged x Glaucous gull hybrids, which suggests a different source population, perhaps a more northerly one, for these later migrants.
DISCUSSION
Herring Gull.
The timing of molt we observed in Herring Gulls is similar to that described by Dwight (1925), but he made no distinctions among the numerous Holarctic taxa in the Herring Gull complex. Our data appear to be the first to describe variation in the timing of first-prebasic molt of L. a. smithsonianus.
Differences in molt timings among North American Herring Gulls may reflect, in part, the nature of their migrations. Largely resident or short-distance migrant populations (such as those along the Atlantic coast [Drury and Nisbet 1972] and in the Great Lakes region [Moore 1076]), can start molting earlier than those populations that undertake longer migrations. Thus, Atlantic coast Herring Gulls are more similar to Western Gulls (Howell and Corben, unpubl. data) in their molt timings than either is to Pacific coast Herring Gulls or Glaucous-winged Gulls presumed to originate from high-latitude populations. Adult Herring Gulls appear to mirror this difference in molt timing. Local-breeding birds in New Jersey attained white-headed alternate plumage by February (D. A. Sibley, pers. comm.), while migrants we observed passing through California in March and April were still in basic plumage. Parallel molt differences have been observed among certain large gulls in Europe. Northern Scandinavian-breeding and longer-distance migrant Herring and Lesser Black-backed Gulls retain juvenal plumage well into the winter, while resident or shorter-distance migrant British populations of the same species undergo their first prebasic molt in autumn and early winter (Golley 1993, Nikander 1996). Furthermore, similar differences in molt timing relative to migration distance have been documented for a variety of other species, including Ringed Plover (Charadrius hiaticula; Prater et al. 1977), tyrant-flycatchers (Pyle 1998), and Old World warblers (Norman 1997).
Differences in molt strategies within and among large gulls thus appear adaptive, and it seems unlikely that they imply phylogenetic significance. The dichotomy in extent of the first prebasic molt in migrant North American Herring Gulls seen in central California may reflect different source populations, perhaps in combination with individual variation, food availability, and the fitness of birds over the winter. Studies at other sites, including marked birds from known populations, could address these factors.
Thayer’s Gull.
Our findings conflict markedly with molt timings given or implied for this taxon by Dwight (1925), Lehman (1980), and Grant (1986), who reported that first basic plumage in this species was attained by November. Nonetheless, molt timing for Thayer's Gull accords well with that of some other Arctic-breeding gulls, namely Glaucous, Iceland, and Kumlien's (L. glaucoides kumlieni) gulls (Devillers 1983b,c; Howell, unpubl. data), and our findings support and amplify the conclusions of McGeehan and Garner (1997) regarding a later onset of first prebasic molt in Thayer's Gull.
Some Thayer's Gulls (and also Iceland and Glaucous Gulls; Devillers 1983b,c) retain apparently full juvenal plumage through the start of their northward migration in late winter. This begs the question (which also applies to some Herring and Glaucous-winged gulls) of the timing and extent of the first prebasic, first prealternate, and complete second pre-basic molts which, given conventional understanding, would occur after birds leave California in April and before they return in November. In this regard, it became apparent during our study (and year-round observations of resident Western Gulls; Howell and Corben, unpubl. data) that feather replacement in first-year large gulls can be an almost continual process. Thus, at what point one draws a line between completion of the first prebasic molt and start of the first prealternate and/or second pre-basic molts can be problematic. Indeed, do first-year large gulls even have a prealternate molt? To answer such questions was beyond the scope of this study. Our observations should be viewed as a preliminary stage, and we hope they will promote fuller analysis and understanding of molt in large gulls.
Glaucous-winged Gull.
The broad range of variation in the timing and extent of first-prebasic molt in this species may relate to the geographic origin of the birds, those from more northerly populations perhaps molting later. Unlike Herring Gulls, there was no strong dichotomy in extent of molt in Glaucous-winged Gulls at any one time, perhaps reflecting the latter species' more-or-less continuous breeding distribution from temperate to subarctic regions. In this regard, the Glaucous-winged Gull may be a good candidate for evaluating correlation between migration and the extent and timing of molt.
While our data do not support those given or implied by other authors (Dwight 1925, Grant 1986) who reported that first-basic plumage in the Glaucous-winged Gull was attained during August to October, our observations relate only to migrants. If locally hatched birds in southern British Colombia and Washington are not strongly migratory (as suggested by Woodbury and Knight 1951) they might commence molt earlier, as do resident Western Gulls in California (pers. obs.).
Logistics.
We note that most molt studies rely heavily upon specimens, and that recent investigators of molt in individual species have lamented the shortage of useful specimens (e.g., Voelker and Rohwer 1998, Yuri and Rohwer 1997). Furthermore, while museum collections usually have extensive series of passerines, this is rarely true of larger birds such as gulls. For example, our sample of 916 first-year gulls would be hard to find in all North American museums combined (cf. 477 examined specimens of Northern Rough-winged Swallows Stelgidopteryx serripennis [Yuri and Rohwer 1997], or 386 of Tree Swallows Tachycineta bicolor [Stutchbury and Rohwer 1990]). In cases where birds are large enough, however, critical field observations, in combination with documentary photographs, the salvage of corpses, and targeted collecting of specimens, can provide large samples and also allow one to follow molt in a population.
Reliance on traditional, seasonal-based terminology may have hindered an understanding of molt in large gulls. Critical observations that age gulls by plumage (as advocated by Humphrey and Parkes 1959), rather than by season, will help to further an understanding of molt and plumage homologies in these under-regarded birds.
 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank David Sibley and Julian Hough for contributing observations and photographs from Cape May, New Jersey, and Strafford, Connecticut, respectively. Sibley also contributed helpful discussions of this complex subject, and the manuscript benefitted from comments by Douglas A. Bell, Peter Pyle, and Sophie Webb. Personnel at the American Museum of Natural History, the Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology, University of California, Berkeley, and the California Academy of Sciences kindly allowed us access to specimens in their care. Michael Lynes assisted with preparation of the figures. This is contribution number 752 of the Point Reyes Bird Observatory.
LITERATURE CITED
 Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 10 2011, Everett, WA. Picture: Steve Mlodinow.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 10 2011, Everett, WA. Picture: Steve Mlodinow. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 30 2011, Tukwila, WA. Picture: Amar Ayyash.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 30 2011, Tukwila, WA. Picture: Amar Ayyash. Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins.
Thayer's Gull juvenile / 1st cycle (1CY), December 14 2008, Half Moon Bay, California, US. Picture: Chris Gibbins. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 10 2013, Half Moon Bay, California. Picture: Alvaro Jaramillo.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 10 2013, Half Moon Bay, California. Picture: Alvaro Jaramillo. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 28 2012, Niagara River, New York. Picture: Amar Ayyash.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle (1CY), December 28 2012, Niagara River, New York. Picture: Amar Ayyash. Thayer's Gull juvenile, December 13 2008, Oceano, CA, US. Picture: Brad Schram.
Thayer's Gull juvenile, December 13 2008, Oceano, CA, US. Picture: Brad Schram. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 19 2010, Hastings, Minnesota, US. Picture: Yann Kolbeinsson.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 19 2010, Hastings, Minnesota, US. Picture: Yann Kolbeinsson. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 25 2011, Navy Pier,
Chicago, Illinois. Picture: Josh Engel.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 25 2011, Navy Pier,
Chicago, Illinois. Picture: Josh Engel. Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 12 2011, Recology Plant, Stanislaus County, CA. Picture: Oscar Johnson.
Thayer's Gull 1st cycle, December 12 2011, Recology Plant, Stanislaus County, CA. Picture: Oscar Johnson. FIRST PREBASIC MOLT IN HERRING, THAYER'S, AND
GLAUCOUS-WINGED GULLS
FIRST PREBASIC MOLT IN HERRING, THAYER'S, AND
GLAUCOUS-WINGED GULLS
S. HOWELL & J. KING
IN: J. Field Ornithol. 1999.
 Figure 1 Timing of first prebasic molt in Herring Gulls (HEGU) wintering in central
California.
Figure 1 Timing of first prebasic molt in Herring Gulls (HEGU) wintering in central
California.
 Figure 2 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Thayer's Gulls (THGU)
wintering in central California.
Figure 2 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Thayer's Gulls (THGU)
wintering in central California. Figure 3 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Glaucous-winged Gulls
(GWGU) wintering in central California.
Figure 3 Timing and extent of first prebasic molt of scapulars in Glaucous-winged Gulls
(GWGU) wintering in central California.












